- 1 INTRODUCTION
- 2 NETWORK PROCESSING IN THE LINUX KERNEL
- 3 TESTBED AND KERNEL CONFIGURATION
- 4 UDP TRANSMISSION
- 5 TCP TRANSMISSION
- 6 TCP TRANSMISSION WITH ZERO-COPY
- 7 THE HARDWARE OFFLOAD FUNCTIONALITIES OF THE NETWORK ADAPTER
- 8 FIBRE CHANNEL TO 10 GIGABIT ETHERNET TESTS
- 9 CONCLUSIONS
本文为摘录,原文为: attachments/pdf/3/performanceOf10GbE.pdf
1 INTRODUCTION
With the introduction of 10-GbE, network I/O re-entered the “fast network, slow host” scenario that occurred with both the transitions to Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet. Specifically, three major system bottlenecks may limit the efficiency of high-performance I/O adapters:
PCI-X 总线带宽
- PCI-X 频率
133MHz,带宽8.5Gb/s - 已被 PCI-Express (PCIe) 替代:
8通道20 Gb/s
- PCI-X 频率
CPU 利用率
内存带宽
2 NETWORK PROCESSING IN THE LINUX KERNEL
2.1 Kernel Accounting
User
- 程序运行在用户态的时间
System
- 程序运行在内核态的时间
IRQ
- CPU 处理硬件中断的时间
SoftIRQ
- CPU 处理软中断的时间
2.2 Packet Transmission 发送
发送队列
- 每个网卡驱动维持一个数据包的发送队列
- 内核根据 qdisc (queue discipline) 将数据包插入到队列中
- 默认的 qdisc 为
pfifo_fast(paccket FIO) - Linux 支持其他的策略, 如
- RED (Radom Early Drop)
- CBQ (Class Based Queuing)
- Others
- 默认的 qdisc 为
link layer
- triggered by function
dev_queue_xmit(), 该函数负责:- 将数据包根据
qdisc插入到发送队列中 - 从发送队列中取出待发送的包,调用驱动的发送函数
hard_start_xmit()来发送 - 如果因为某些原因 (如设备没有资源了),它会安排 SoftIRQ , 然后晚些通过软中断再次发送
- 将数据包根据
- triggered by function
设备驱动
- 设备驱动负责将数据从
tx_ring中转移到网卡的缓冲区中 - 该操作通过设置 DMA 映射,然后设置硬件上的特定寄存器来完成
- 驱动无需等待发送完成:
- 发送完成之后硬件发出硬中断
DMAdone - 内核收到中断后安排 SoftIRQ 来释放 packet 使用的内存 释放内存操作耗时相对较长,不适合在硬中断中完成
- 发送完成之后硬件发出硬中断
- 设备驱动负责将数据从
2.3 Packet Reception 接收
接收从 NIC 开始。
- NIC
- 接收到一对 Ethernet frames
- Frames 存储在
rx_ring- 内核 reserved 空间中
- 环形缓冲区
- 网卡将接收到的数据放到 DMA 后,将中断信号发送给指定的 IRQ line
- 中断控制器负责中断指定的处理器
2.4 Incorrect SoftIRQ Accounting
3 TESTBED AND KERNEL CONFIGURATION
测试机配置和网络拓扑:

内核参数:
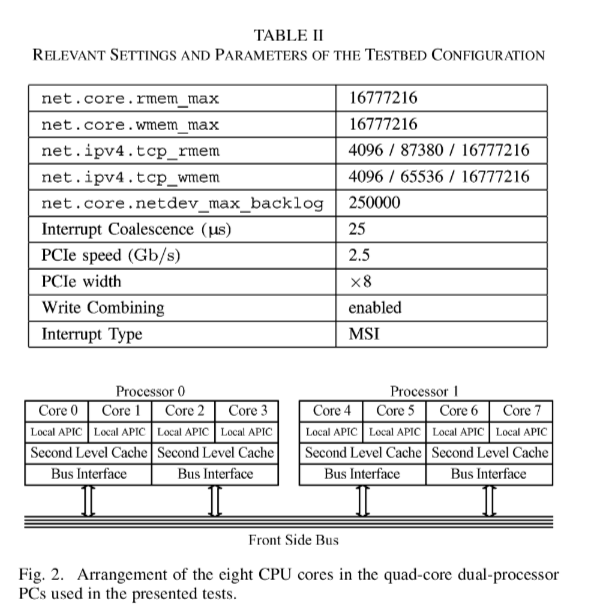
net.core.rmem_max,net.core.wmem_max接收端和发送端 socket buffer sizenet.ipv4.tcp_rmem,net.ipv4.tcp_wmem接收端和发送端 tcp buffer size (min, default, max)net.core.netdev_max_backlog控制软中断函数net_rx_action()每次处理的数据包的个数
4 UDP TRANSMISSION
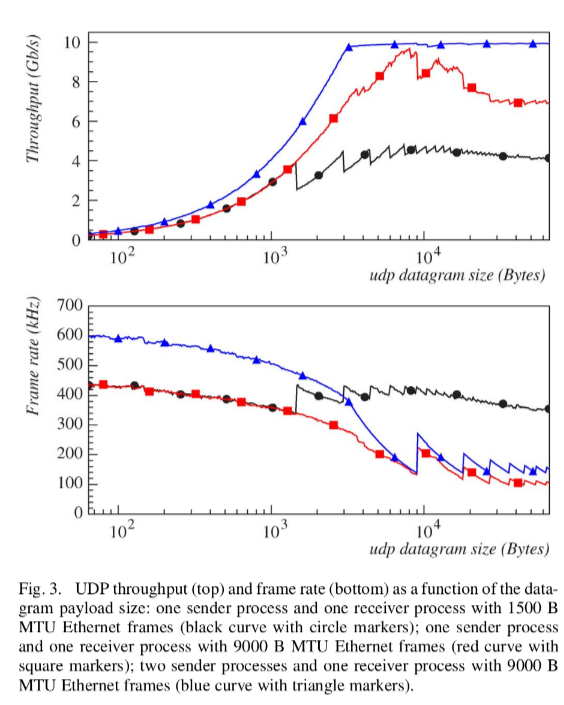
- 两个发送进程,MTU 9K 时候性能最好
- MTU 9K 时候, packet size 8K 以上可以跑满
5 TCP TRANSMISSION
shows the data transfer rate, measured as a function of the TCP send size. For a MTU of 1500 B, the maximum throughput achieved was around 5.5 Gb/s, reached at the max- imum tested send size of 64 KiB. The throughput decreased as decreased the send size, with a change in the slope at 1500 B. The adoption of the 9000 B MTU with TCP improved the throughput up to 7 Gb/s.

6 TCP TRANSMISSION WITH ZERO-COPY
sendfile()来省略在内核态与用户态之间的数据拷贝5.5 Gb/s->8Gb/s
7 THE HARDWARE OFFLOAD FUNCTIONALITIES OF THE NETWORK ADAPTER
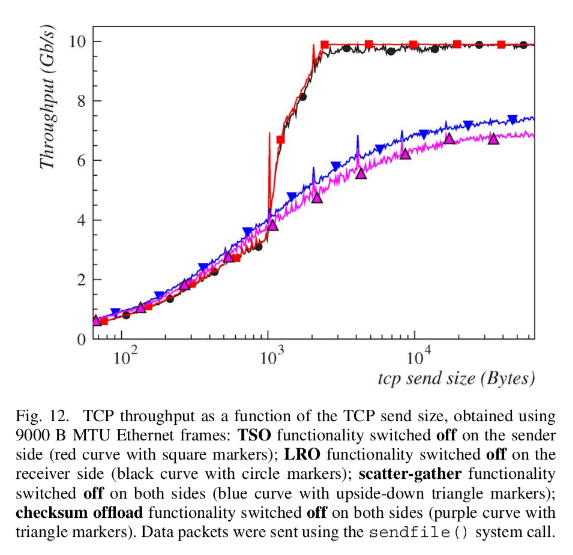
offload function: 内核可以将高负载的任务交给硬件去做。
TCP Segmentation Offload, TSO
- 工作在发送端
- 当 TCP 的数据包大小超过 MTU 时候,必须进行分片操作
- 不支持 TSO 的硬件,必须由内核在 TPC 层完成
- 支持 TSO 的硬件,则可将最大
64K的数据一次性交给网卡,由网卡来完成分片
Large Receive Offload, LRO
- 工作在接收端
- 在 NIC 层将多个 TCP packets 重组成更大的数据包
Scatter-Gather (SG) I/O
- 可以将不连续的内存地址通过 DMA 映射,减少内存拷贝
Checksum Offload, CO
- TCP 包的 checksum 计算
这些 offload 的效果:
吞吐量结果:
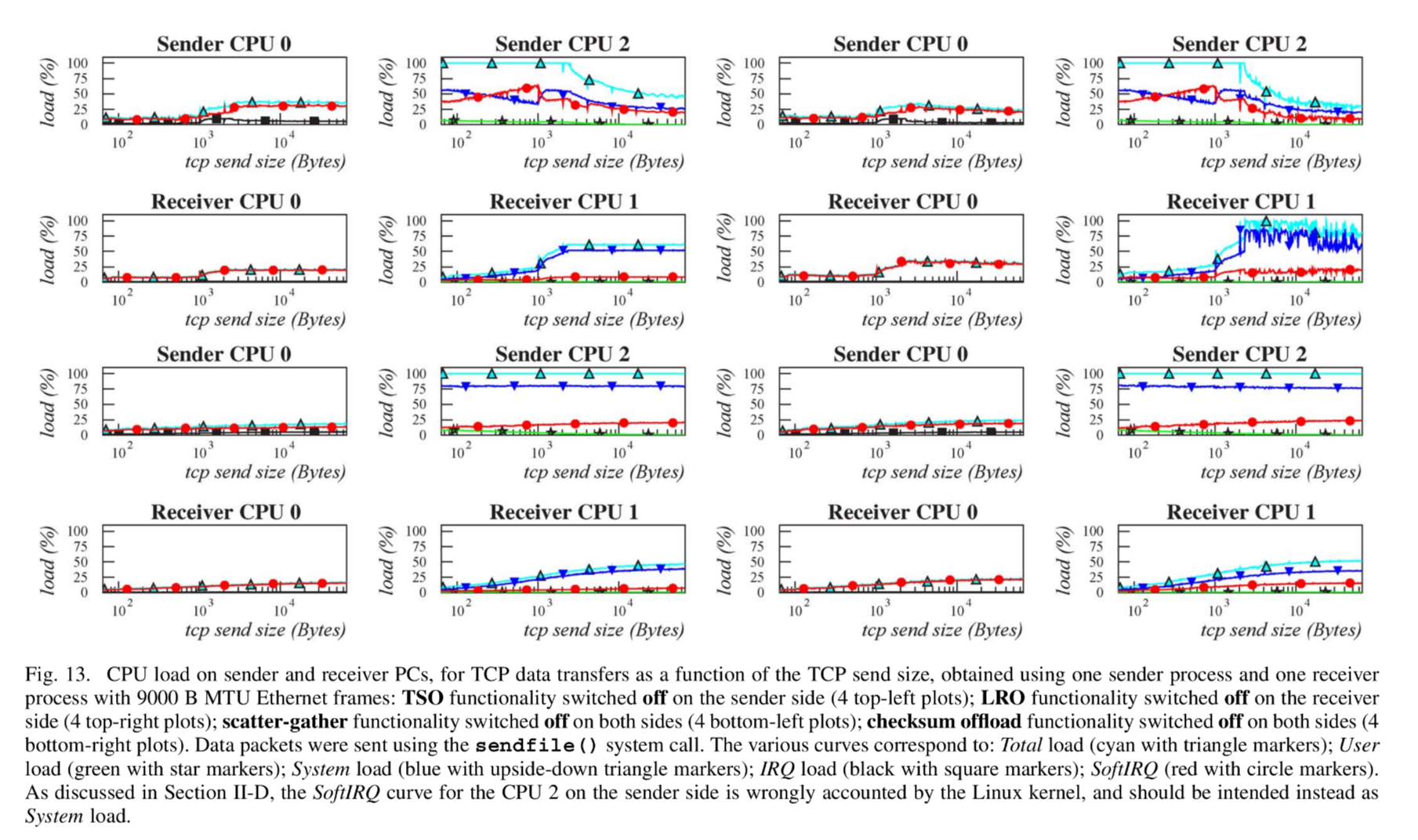
CPU 负载:
8 FIBRE CHANNEL TO 10 GIGABIT ETHERNET TESTS
9 CONCLUSIONS
- MTU matters
- Offload matters…